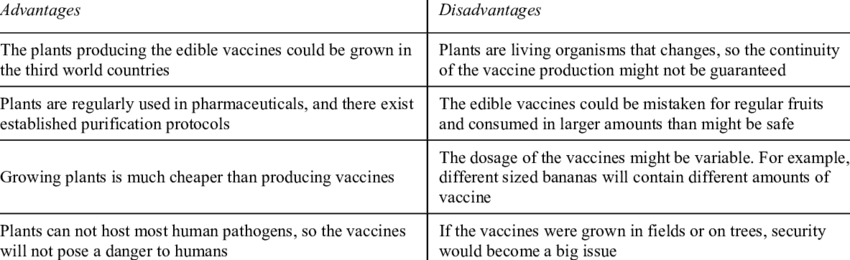
Edible vaccines offer multiple advantages over traditional vaccines. They are administered orally, eliminating the discomfort of injections and improving patient compliance. Their production is cost-effective, scalable, and does not require complex manufacturing facilities. Being heat-stable, they do not need cold storage, making them ideal for regions with limited healthcare infrastructure. Additionally, they reduce dependency on trained healthcare personnel and can be produced locally, enabling faster responses to outbreaks. By integrating vaccine production into food supply chains, edible vaccines could address logistical challenges and ensure widespread accessibility, especially in developing countries where traditional vaccination programs face barriers.
